Multiple Sclerosis
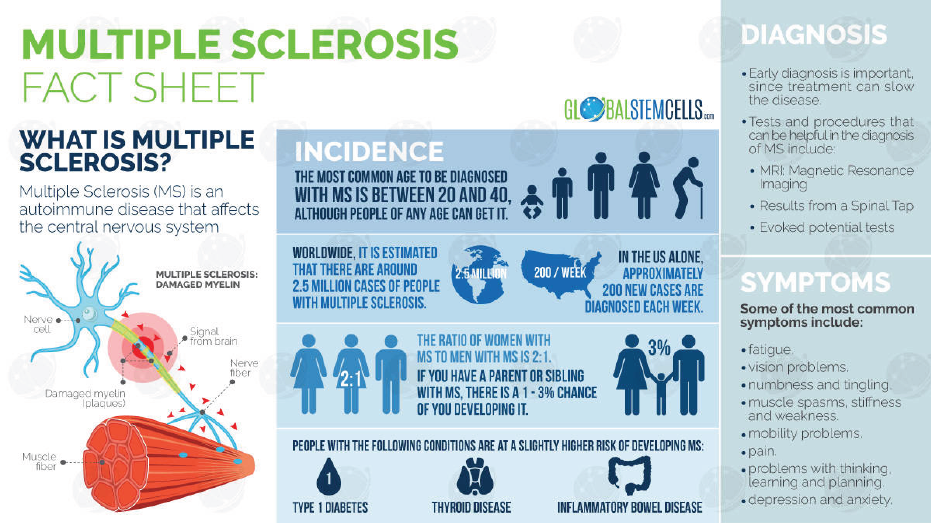
Fighting Autoimmune Disease
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is initiated when the body incorrectly mounts an immune response against its own tissues. It affects a range of biological systems and has fluctuating patterns of activity and remission as shown on the right.
A diagnosis of MS can be frightening and overwhelming.
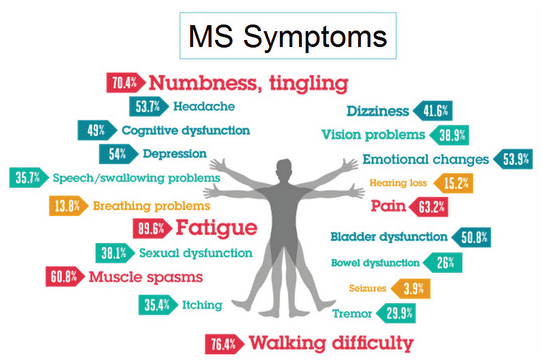
The Need For A Personalised Approach
Low Dose Naltrexone (LDN)
A small dose of the drug taken nightly at bedtime triples the endorphin levels in the body all of the next day restoring levels to normal. Since endorphin levels are low in people with MS, immune function is poorly orchestrated with significant impairment of the normal immune supervisory function of CD4 cells. In the absence of normal orchestration of immune function, some of the immune system cells "forget" their genetically determined ability to distinguish between the body's 100,000 unique chemical structures (called "self") and the chemical structures of bacteria, fungi, parasites and cancer cells (called "non-self"). With this loss of immunologic memory, some cells begin to attack some of the body's unique chemical structures. In the case of people with MS, the tissue attacked by immune cells (particularly macrophages) is primarily the myelin that insulates nerve fibers. These attacks result in scars in the brain and spinal cord called plaques. LDN in such patients works by restoring endorphin levels to normal, thereby allowing the immune system to resume its normal supervision and orchestration.
Endorphins are almost all produced in the middle of the night, between 2 AM and 4 AM. Studies focused on small doses (1.5-4.5 mg at bedtime) with the hope that a brief period of endorphin blockade before 2 AM might induce an increase in the body's endorphin production. In fact, the drug did so in this dosage range. It had no effect below 1.5 mg and too much endorphin blockade at doses over 5 mg. Patients taking low-dose naltrexone report decreased progression in their disease with fewer exacerbations, arm-pain relief, improved bladder control, less fatigue, reduction in numbness in lower legs and feet, reduction in stiffness and muscle spasms, and reduction in dizziness and slurred speech.
Multiple Sclerosis Journal - Experimental, Translational and Clinical 2016;2:1-11.Ludwig MD, et al. Long-term treatment with low dose naltrexone maintains stable health in patients with multiple sclerosis.
Multiple Sclerosis 2010;16(8):964-969. Sharafaddinzadeh N, et al. The effect of low-dose naltrexone on quality of life of patients with multiple sclerosis: a randomized placebo-controlled trial.
4-Aminopyridine
Another compound prescription for MS is 4-Aminopyridine (4-AP). 4-AP is a drug shown to improve visual function and motor skills and relieve fatigue in MS patients. 4-AP is most effective in patients with a chronic progressive form of MS, in patients who are temperature-sensitive, and in patients who have had MS for longer than three years. Common side effects include dizziness, nervousness and nausea, and the incidence of adverse effects was shown to be less than 5% in all studies. 4-AP works as a potassium channel blocker. Electrophysiologic studies of demyelinated axons show that abnormal potassium currents decrease action potential duration and amplitude and contribute to conduction failure. Potassium channel blockade prolongs the repolarization phase of the action potential, increasing conductivity along the demyelinated axon. MS patients treated with 4-AP exhibited a response rate of 29.5% to 80%. A 32 month study indicated that 80%-90% of patients who initially responded to 4-AP exhibited long-term benefits. Although improving symptoms, 4-AP does not inhibit progression of MS. Spinal cord injury patients have also seen improvement with 4-AP therapy. These improvements include sensory, motor and pulmonary function, with a decrease in spasticity and pain.
Biotin
A global Phase 3 clinical trial assessing high-dose biotin (MD1003) — for progressive multiple sclerosis might lead to the approval of one of the first treatments helping select progressive patients to improve. Biotin is essential for fatty acid synthesis and energy production. Biotin 300mg daily:-
improved MS-related disability in an open-label study promote axonal remyelination by enhancing myelin production reduce axonal hypoxia through enhanced energy production reported reduced pain and improved energy levels 1 vision had improved 2 documented an improvement in vision as well as a reduction in partial paralysis. In another study, 91 percent of participants showed clinical improvement
It is important to note that these are preliminary studies and that not every person who took part in the studies saw the same degree of improvement. However, several studies do show that of those people who have been treated with high levels of biotin, some have seen a slow-down in the progress of the disease and an improved quality of life.
- Neurology April 5, 2016 vol. 86 no. 16 Supplement P3.039
- Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2015 Mar;4(2):159-69
- https://mssociety.ca/research-news/treatments-in-development/md1003
 Contact Us
Contact Us

